The function of a protein being a direct consequence of its 3-D structure (shape), the logical link was established.
Sequence>>Structure>>Function
It is now a central concept of molecular biology devoted bioinformatics. As a consequence, an increasing proportion of the bioinformatics pie is now devoted to the development of tools to navigate between sequences and 3-D structures. (This specialized area is called structural bioinformatics.)
Use the assigned unknown sequence to explain the concept of ‘Structural Bioinformatics’.
There are three relationships of the assigned unknown sequence.
1. Sequence:
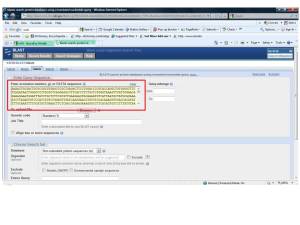
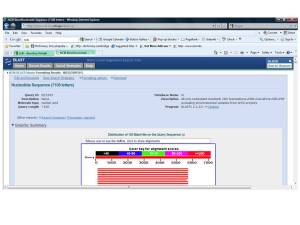
1.1 Search the assigned nucleotide sequence by using blastx (search protein database using a translated nucleotide query).
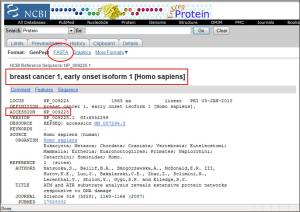
1.2 Descriptions: sequences producing significant alignments. Accession number NP_009225 with the definition of breast cancer 1, early onset isoform1 (Homo sapiens) was selected because of the best score (Bits). Then click the accession number to get FASTA protein sequence.
The output is the FASTA protein sequence which is further used to analyse the structure.
2. Structure:
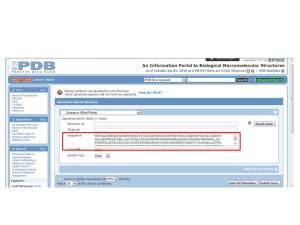
2.1 Search the structure of assigned unknown sequences by using Protein Data Bank (PDB) database, then click sequence search tab.
2.2 Then put the FASTA protein sequence in the sequence box.
The output is shown below. Crystal Structure of the BRCT Domains of Human BRCA1 in Complex with a Phosphorylated Peptide from Human Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase 1 was selected.
3. Function:antitumor protein/ligase
The human BRCA1 protein is a tumor suppressor and is involved in multiple cellular functions, such as DNA repair, cell cycle checkpoint control, transcription and ubiquitination. The tandem BRCA1 C-terminal (BRCT) domains are phospho-serine/threonine recognition modules essential for the function of BRCA1. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 (ACC1), an enzyme with crucial roles in de novo fatty acid biosynthesis and lipogenesis and essential for cancer cell survival, may be a novel binding partner for BRCA1, through interactions with its BRCT domains. As the BRCA1-ACC1 complex has reduced activity for fatty acid biosynthesis , these suggest a cytoplasmic component for BRCA1’s function as a tumor suppressor. Mutations in the BRCT domains of BRCA1 can abolish the regulation of ACC1 and lead to elevated lipogenesis, which is an important requirement for cancer cell growth.
(Reference: Yang Shen and Liang Tong. Structural evidence for direct interactions between the BRCT domains of human BRCA1 and a phospho-peptide from human ACC1. Biochemistry 2008 May 27; 47(21): 5767–5773.)